Intelligent Systems
Table of Contents
Rational agents
“A rational agent chooses whichever action maximizes the expected value of the performance measure given the percept sequence to date and prior environment knowledge.”
Agents
agent function maps percept sequence to actions ($f: P* \rightarrow A$)
function is internally represented by agent program
program runs on physical architecture to produce f
Rationality
what is rational at a specific time depends on: * expected value of performance measure – heuristics * actions and choices – search * percept sequence to date – learning * prior environment– KR
rationality is not omniscience or perfection
Task environments
to design rational agent, we must specify environment (PEAS): * performance: safety, destination, profits, legality, comfort * environment: streets, traffic, pedestrians, weather * actuators: steering, accelerating, brake, horn, speaker/display * sensors: video, sonar, speedometer, etc.
environment types: * observable: fully (can detect all relevant aspects with sensors) or partially * deterministic: (yes or no) * static: (yes, no, semi) * discrete: (yes or no) * single-agent: (yes or no)
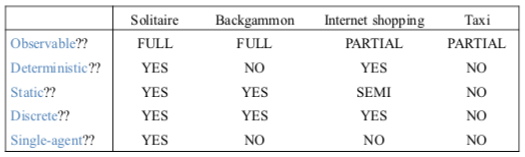
For Schnapsen:
- observable: not fully
- deterministic: yes
- static: yes
- discrete: yes
- single-agent: no
Agent types
Simple Reflex
select action on basis of only the current percept
large reduction in possible percept/action situations
implemented using condition-action rules
only works if environment is fully observable, otherwise may result in infinite loops.
Reflex & State
to tackle partially observable environments, maintain internal state
over time, update state using world knowledge.
Goal-Based
agent needs a goal to know the desirable situations
future is taken into account
Learning
teach agents instead of instructing them
very robust toward initially unknown environments.