Operating Systems
Table of Contents
Process model
process: program in execution (amount of processes depends on the program)
it’s an abstraction that allows OS to simplify resource allocation, accounting, and limiting.
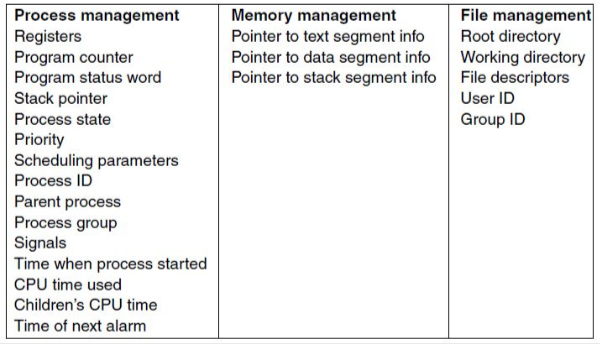
Process table
OS maintains info on resources and internal state of every process
information in Process Table: ID (PID), User (UID), Group (GID), memory address space, hw registers, open files, signals, etc.
process control blocks:
Concurrent processes
in principle, multiple processes are mutually independent (they have nothing at all in common). need explicit means to interact with each other.
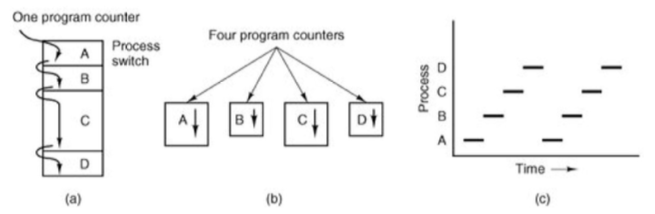
the CPU gets allocated to each process in turn
- on OS level: save context of process A (program counter, registers, etc.), switch to B. to go back to process A, simply restore context.
OS (normally) offers no timing or ordering guarantees
Process hierarchies
OS creates only 1 init process (usually) parent process can create a child process results in a tree-like structure and process groups
Process management
fork: create new process
- child is ‘private’ clone of parent
- shares some resources with parent
exec: execute new process image
- used in combination with fork
- replaces the current command
exit: cause voluntary process termination
- exist status returned to parent process
kill: send signal to process (or group)
- can cause involuntary process termination
Process states
OS allocates resources to processes three process states:
- running: process is currently executed by CPU
- blocked: process is waiting for available resources
- ready: process is ready to be selected

scheduler allocates/deallocates the CPU. there is no immediate transition between states because process has to wait for scheduler
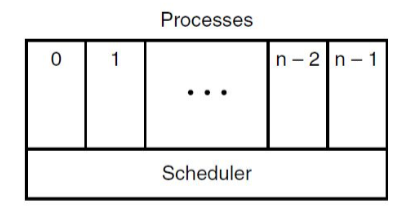
Scheduler vs processes
- scheduler periodically switches processes
- sequential processes lie on the layer above
- leads to simple process organisation