Software Architecture
Table of Contents
Introduction
What is software architecture?
- fundamental concepts/properties of system in its environment
- embodied in its elements, relationships, and principles of its design/evolution
- so: design + design decisions
Why?
- vehicle for stakeholder communication
- way for manager to reason about cost and schedule
- manifests earliest set of design decisions
- transferable abstraction of system
Characteristics of Software Architecture
- Iteration on functional/quality requirements
- Many stakeholders involved
- Balancing of functional/quality requirements
Architecturally significant requirements (ASRs):
- architectures are driven by quality attribute requirements (e.g. system must be modular, shall meet users’ performance expectations)
- features/functionality shape architecture to lesser extent
Business goals:
- e.g. “we want to differentiate our product from competition and capture market share)
- may directly affect architecture
- often lead to quality attribute requirements
Architecture representations & styles
Structure: coherent set of architectural elements View: representation of structure (picture)
Structures:
- modules: module is unit of implementation with assigned areas of functionality
- component-connector: elements with runtime behavior (components) and interactions (connectors)
- allocation: relationship between software elements and environment
Architectural style: description of component and connector types, pattern of their runtime control/data transfer
Design patterns: recurring structures of communicating components that solve general design problem in a context (e.g. Model-View-Controller)
Architecture assessment
Assesses whether architecture meets quality goals.
Software Architecture Analysis Method (SAAM)
- develop scenarios for
- activities system must support
- changes anticipated
- describe architectures
- classify scenarios
- direct: use requires no change
- indirect: use requires change
- evaluate indirect scenarios wrt changes and cost
- reveal scenario interaction
- overall evaluation
Architecture influence cycle
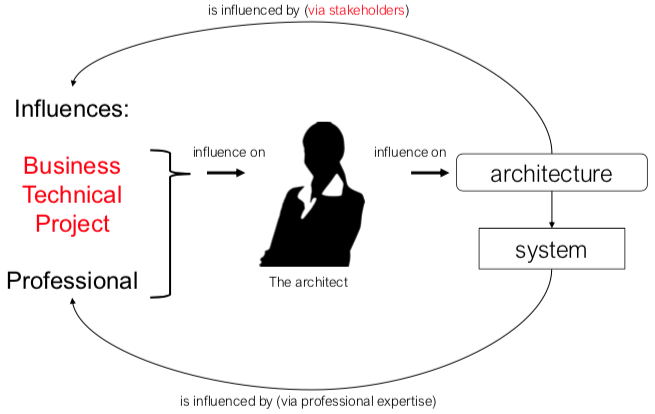
architecture affects:
- structure of developing organisation
- goals of developing organisation
- requirements for next systems
Building a system affects architect’s experience
Role of software architect
Ineffective: police agent, documentalist, isolationist (no communication with stakeholders) Effective: key tech consultant, decision maker, coach of dev team, design coordination, implementing key parts
A good architect (1) has experience, (2) has domain knowledge, (3) communicates.